Website speed is very important for how well your site works. It affects how visitors use your site, how high your site ranks on search engines, and even how likely people are to become customers. A slow website can hurt your business in many ways – it can drive visitors away, lower your search engine ranking, and lead to fewer sales.
In this guide, we’ll explain why website speed matters and how you can make your site load faster. We’ll show you how to test website loading speed and give you easy tips to optimise website loading speed. By following these steps, you can make sure your visitors have a fast and smooth experience on your website.
Why Website Speed is Important
Before we talk about how to improve your website speed, it’s helpful to understand why it’s so important. Faster websites make users happy and lead to better results. On the other hand, slow websites can drive visitors away and hurt your search engine ranking and conversion rates. In this section, we’ll cover:
- User Expectations: Visitors expect websites to load quickly, and delays can frustrate them, causing them to leave.
- Search Engine Rankings: Google and other search engines favour fast websites, which can help your site rank higher.
- Conversions: Website speed affects how likely visitors are to make purchases, sign up for services, or take action on your site.
- Mobile Traffic: More people are browsing on mobile devices, so it’s important to make your website load quickly on phones and tablets.
Expected Website Speed
Website speed optimisation involves techniques to make your website load as quickly as possible. Some key measures of website speed are:
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): How long it take for the server to send the first response?
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): The time it takes for the first text or image to show up.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How long it takes for the biggest element, like a large image or heading, to load.
- Page Load Time: How long it takes for the entire page to fully load on the screen.
For a smooth user experience, aim for these targets:
- TTFB: Under 0.8 seconds
- FCP: Under 1.8 seconds
- LCP: Under 2.5 seconds
- Page Load Time: Under 3 seconds
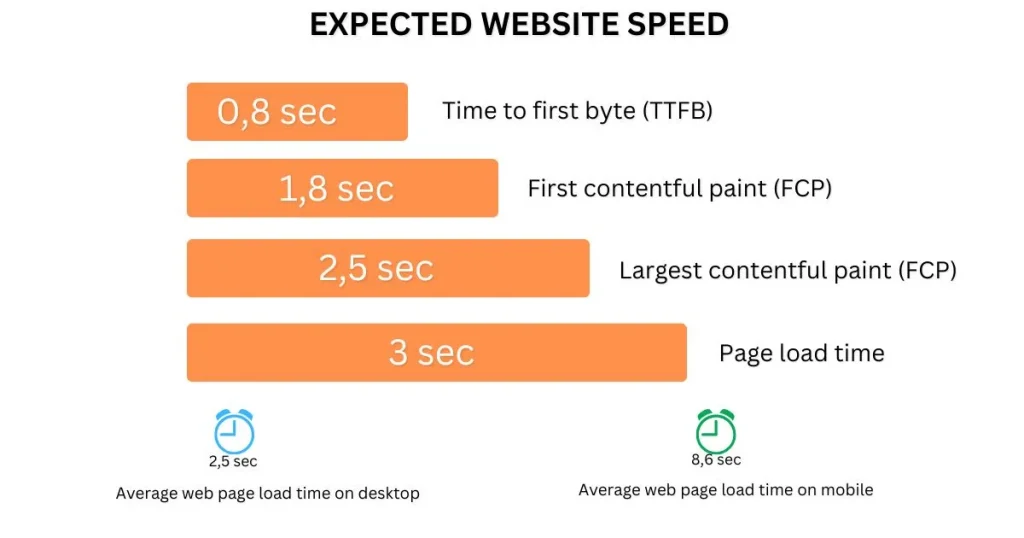
Interestingly, a study of the top 100 websites found the average page load time was 2.5 seconds on desktop and 8.6 seconds on mobile.
What Affects Website Loading Speed?
Before we look at solutions, it’s important to understand the common factors that make websites slow. Here’s a quick rundown:
1. Large Images
High-resolution images can take up a lot of space, which means they take longer to load. When these files aren’t optimised, they slow down the entire website.
2. Unoptimised Code
Websites run on code, such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. If this code is messy or filled with unnecessary elements, it can bog down the site.
3. Server Response Time
Your web server is responsible for delivering your website to visitors. If the server is overloaded or poorly configured, it will take longer to respond to requests.
4. Too Many Plugins
For websites built with platforms like WordPress, plugins can extend functionality. However having too many or poorly coded plugins can slow everything down.
5. No Browser Caching
Browser caching lets visitors store parts of your website (like images or CSS files) on their local device. Without caching, these elements need to reload every time someone visits your site.
6. Excessive Redirects
Redirects take users from one URL to another. While they can be necessary, too many of them increase load times.
7. Ads and Third-Party Tools
Running ads or integrating third-party tools can lead to extra requests and scripts, adding load time to your pages.
How to Measure Your Website Speed
Before you can make your website load faster, you need to know how fast it loads right now. Measuring your site’s speed will help you understand what needs to be improved. There are many free tools you can use to check your website’s speed and see where it can be faster. Let’s take a look at some of the most popular ones:
Google PageSpeed Insights
Google’s PageSpeed Insights is a free tool that checks how fast your website loads. It gives you a score for both mobile and desktop versions of your site and provides suggestions on how to make it load faster.
GTmetrix
GTmetrix is another great tool that gives you a detailed report about your website’s speed. It shows how fast your site loads, how big the page is, and how many requests are made. GTmetrix also gives you tips on what you can do to make your website load faster.
Pingdom
Pingdom lets you check your website speed from different places around the world. It tells you how long it takes for your website to load, and what things (like images or scripts) are slowing it down. It also gives you suggestions on how to make your site faster.
WebPageTest
WebPageTest is a powerful tool that checks your site’s speed from different locations and browsers. It shows you exactly how long it takes for your site to load, and how long it takes to start loading (called Time to First Byte), and gives you details about how different parts of your website are performing.
Performance Budget Calculator
The Performance Budget Calculator helps you set goals for how fast your website should load. A “performance budget” is like a limit or goal for how big your website can be and how many things (like images or files) it should load. Using this tool helps you make sure your website is not too slow.
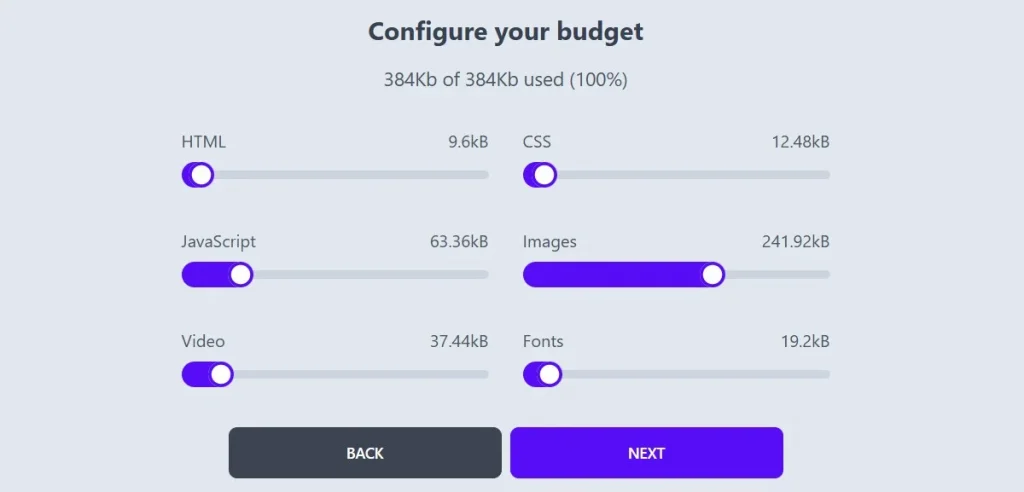
Use the Performance Budget Calculator to set your budget. Source: Performance Budget Calculator.
How to Improve Website Performance
Website performance is critical to the success of any online business. A slow website can result in high bounce rates, lower user engagement, and a poor reputation. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can implement to optimise website loading speed. In this guide, we’ll walk you through 12 proven methods to optimise your site’s speed and enhance its overall performance.
1. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a network of servers located in various locations around the world. Instead of loading your website from a single server, a CDN ensures that content is delivered from the server closest to the user, reducing the time it takes for the site to load. CDNs store cached copies of your site’s static files (like images, stylesheets, and JavaScript) on servers across the globe. When a user accesses your website, the CDN serves those files from the nearest server.
Why It Works:
- Faster Load Times: The closer the server is to the user, the quicker it will load your website, helping to optimise Website Loading Speed.
- Reduced Latency: By distributing content closer to your audience, CDNs reduce latency (delay in data transfer) and improve load times.
- Improved Reliability: CDNs help prevent server overload by distributing traffic, ensuring that even if one server goes down, others can take over.
How to Set It Up:
- Choose a CDN provider like Cloudflare, Amazon CloudFront, or StackPath.
- Set up your website with the CDN by linking it to your hosting provider or configuring it through your CMS (like WordPress).
- After setup, the CDN will automatically serve cached versions of your website to users based on their location, further helping to optimise Website Loading Speed.
2. Move Your Website to a Better Host
Your website hosting provider plays a major role in how quickly your website loads. Shared hosting, while affordable, often leads to slower speeds due to limited resources and overcrowded servers. If your site is slow, consider upgrading to a better hosting option.
Why It Works:
- Faster Server Resources: A better host, such as a Virtual Private Server (VPS) or dedicated server, ensures your website gets the resources it needs.
- Improved Uptime: A high-quality host offers better reliability, reducing the chances of downtime, which can negatively affect performance.
How to Choose the Right Hosting:
- Look for hosts offering SSD (Solid State Drive) storage over HDD (Hard Disk Drive). SSDs are faster and more efficient.
- Choose VPS or dedicated hosting if you have high-traffic or resource-intensive sites.
- Look for managed hosting services that offer built-in optimisation and support to optimise Website Loading Speed.
3. Optimise the Size of Images on Your Website
Images are one of the most common culprits behind slow website load times. High-resolution images can be very large, slowing down your site. Optimising images ensures that they load faster without compromising quality.
Why It Works:
- Reduced File Size: Optimising images reduces their file size, making them quicker to load.
- Improved User Experience: Faster load times lead to a better user experience, especially on mobile devices.
How to Optimise Images:
- Use Image Compression: Tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or Photoshop can reduce the size of your images while maintaining quality.
- Choose the Right File Format: Use JPEG for photographs and PNG for graphics with fewer colours. WebP is also a modern, efficient format supported by most browsers.
- Resize Images: Avoid uploading oversized images. Resize them to the maximum dimensions needed for your website to optimise Website Loading Speed.
4. Reduce the Number of Plugins
Plugins are great for adding functionality to your website, but too many can slow it down. Some plugins are poorly coded, and others may load unnecessary scripts and styles, adding to your page’s load time.
Why It Works:
- Less Overhead: Fewer plugins mean fewer resources are used, which can help your website run faster.
- Improved Site Stability: Reducing plugins minimises the chances of conflicts or bugs that could slow your site down.
How to Optimise Plugins:
- Audit Your Plugins: Regularly review your installed plugins and remove any that are unnecessary or redundant.
- Use Lightweight Plugins: Choose well-coded, lightweight plugins that don’t add unnecessary bloat to your website.
- Keep Plugins Updated: Ensure your plugins are always up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.
5. Minimise the Number of JavaScript and CSS Files
Each JavaScript and CSS file your website loads adds extra time to the page load. The fewer these files, the faster your website will load. Minifying these files can also reduce their size and improve site performance.
Why It Works:
- Fewer HTTP Requests: Minimising the number of JavaScript and CSS files reduces the number of HTTP requests, speeding up your site.
- Smaller Files: Minification removes unnecessary spaces and characters in the code, reducing the size of the files and making them load faster.
How to Minify JavaScript and CSS:
- Combine Files: Merge multiple CSS and JavaScript files into a single file to reduce requests.
- Use a Minification Tool: Tools like UglifyJS (for JavaScript) or CSSNano (for CSS) can automatically minify your code.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Cache your minified files in the browser so users don’t need to reload them with every visit.
6. Use Website Caching
Caching stores a copy of your website on a user’s device, so they don’t have to load it from scratch every time they visit. This can significantly improve loading times for repeat visitors.
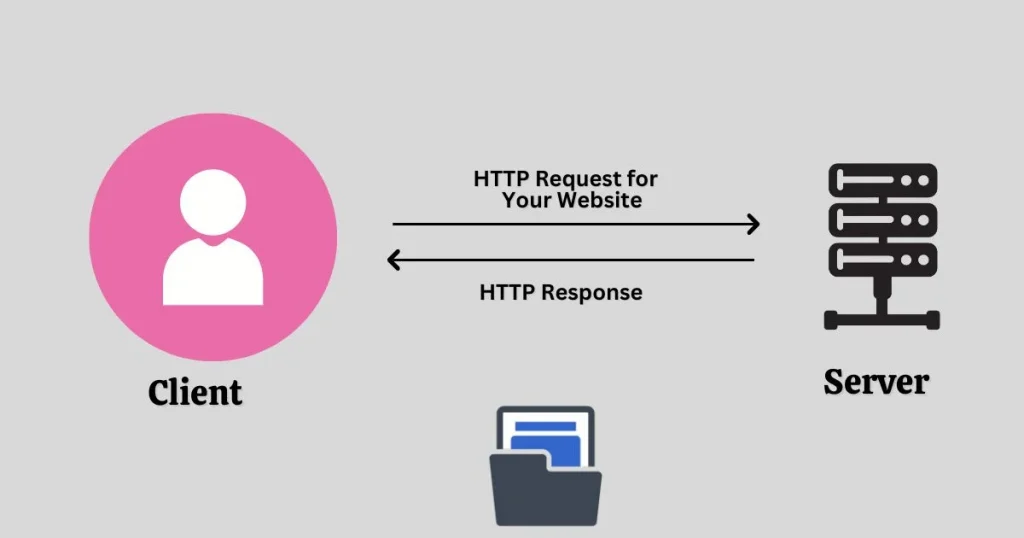
Why It Works:
- Faster Load Times for Repeat Visitors: Cached pages load much faster because the browser doesn’t need to request all files from the server again.
- Reduced Server Load: Caching reduces the strain on your server, as static content is delivered directly from the browser’s cache.
How to Set Up Caching:
- Use a Caching Plugin (For CMS like WordPress): Plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Super Cache allow you to easily enable caching on your site.
- Set Expiry Dates: Use proper cache expiry headers to tell browsers how long to store content.
- Enable Object Caching: Object caching stores dynamic content (like database queries) to reduce server processing time.
7. Implement GZIP Compression
GZIP compression reduces the size of your website’s files, speeding up the process of transferring them from your server to the user’s browser. It’s supported by most modern browsers and can have a significant impact on load times, contributing to optimising Website Loading Speed.
Why It Works:
- Smaller File Sizes: GZIP compresses files, reducing their size by up to 70%, which leads to faster downloads.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Since files are smaller, your website will use less bandwidth, saving you on hosting costs.
How to Implement GZIP Compression:
- Enable GZIP on Your Server: Most servers support GZIP compression by default, but you can check and enable it via your server’s .htaccess file or by contacting your hosting provider.
- Use a Plugin (For CMS like WordPress): WordPress users can use plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Rocket to enable GZIP compression.
8. Optimise a Database in CMS
If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, your website relies on a database to store content and settings. Over time, databases can become bloated with outdated information, slowing down your site.
Why It Works:
- Faster Queries: A clean and optimised database allows your site to retrieve data faster, reducing load times.
- Better Performance: Optimising your database can also reduce server load and improve overall site performance.
How to Optimise Your Database:
- Use a Database Optimisation Plugin: WordPress users can use plugins like WP-Optimise or WP-Sweep to clean up and optimise their database.
- Remove Unnecessary Data: Delete old post revisions, trashed posts, and unused tables.
- Schedule Regular Database Optimisations: Set up automatic cleanups to optimise your database regularly.
9. Reduce the Use of Web Fonts
Web fonts are often used for custom typography, but each web font you use adds extra HTTP requests, which can slow down your website. Reducing the number of web fonts can improve your site’s speed.
Why It Works:
- Fewer HTTP Requests: Reducing the number of web fonts reduces the number of requests the browser needs to make, speeding up the page load.
- Smaller File Sizes: Some web fonts are quite large, and minimising their use can reduce page weight.
How to Use Web Fonts Efficiently:
- Limit the Number of Fonts: Use one or two fonts across your website instead of multiple font families.
- Use System Fonts: Consider using system fonts (like Arial or Times New Roman) instead of web fonts, which don’t require additional requests.
- Use Font Subsetting: Only load the characters your website needs, rather than the entire font set.
10. Detect 404 Errors
404 errors (page not found) can lead to a poor user experience and increased load times. Broken links not only frustrate visitors but also negatively impact your SEO.
Why It Works:
- Improved User Experience: Fixing broken links helps users navigate your site without encountering frustrating error messages.
- SEO Benefits: Eliminating 404 errors improves the search engine crawlability of your site.
How to Detect and Fix 404 Errors:
- Use a Broken Link Checker: Tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console can help you identify 404 errors.
- Redirect Broken Links: Use 301 redirects to point broken links to relevant pages.
11. Reduce Redirects
Redirects are useful for guiding users to new URLs, but they can slow down your website because each redirect creates an additional HTTP request and response cycle.
Why It Works:
- Fewer HTTP Requests: Reducing redirects minimises the number of requests the browser has to make, improving load time.
- Better User Experience: Redirects can cause delays and may confuse users.
How to Reduce Redirects:
- Fix Internal Links: Ensure your internal links are pointing directly to the correct URLs without unnecessary redirects.
- Avoid Excessive Redirect Chains: Make sure redirects aren’t chained together, as this increases load time.
12. Use Prefetching Techniques
Prefetching allows browsers to load resources before they’re needed, which can speed up navigation across your website.
Why It Works:
- Faster Navigation: By preloading certain resources, the browser can access them instantly when needed, improving the user experience.
- Reduced Load Times: Prefetching techniques can reduce waiting time for users as they click through different pages of your site.
How to Implement Prefetching:
- Link Prefetching: Use the <link rel=”prefetch”> HTML tag to tell the browser to fetch resources that will be needed later.
- DNS Prefetching: Use <link rel=”dns-prefetch”> to resolve domain names before they are needed.
Conclusion and Final Tips
Improving your website’s speed is an ongoing task that needs regular checking and updates as technology changes. By using the strategies in this guide, you can make your website load faster and provide a better experience for visitors. To keep your site performing well, make sure to check its speed often and fix any issues that come up. Focus on both server-side improvements, like better hosting and caching, and client-side fixes, such as reducing image size and removing unnecessary scripts. Also, keep up with the latest web technologies to make sure your website stays fast and competitive. By staying on top of these steps, your site will continue to perform well and offer a smooth experience for users.

 Our company was established
since 2009
Our company was established
since 2009